Resources
CGH Alignment Patterns Directory
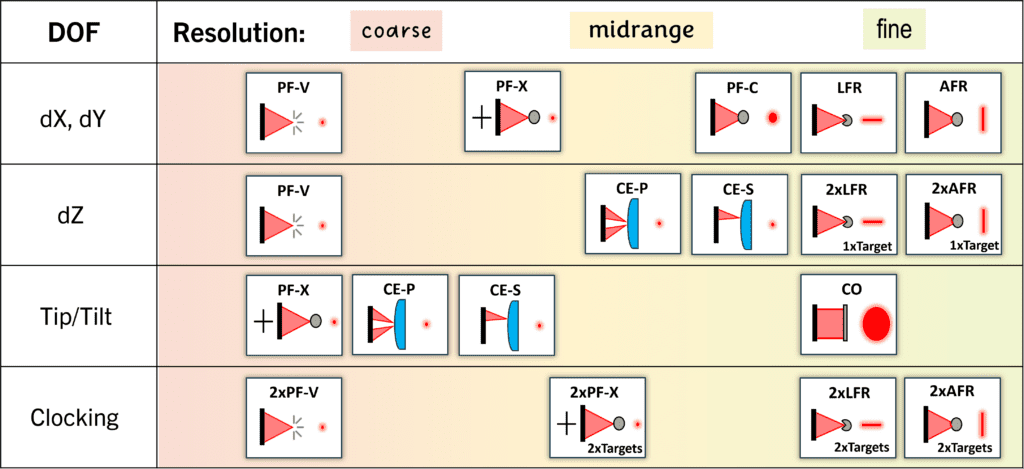
A summary of AOM CGH alignment patterns is shown below. Each pattern is linked to a page that describes it in more detail.
| Alignment Pattern Name & ID | Symbol | Typical Target Used | DOF and Sensitivity | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Visual Point Focus (PF-V) | 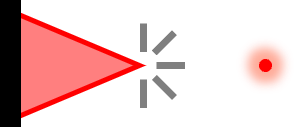 | Diffuse surface or UUT | Coarse dX, dY, and dZ | Projects a focused spot to reference feature for visual alignment aid. |
| Collimation (CO) | 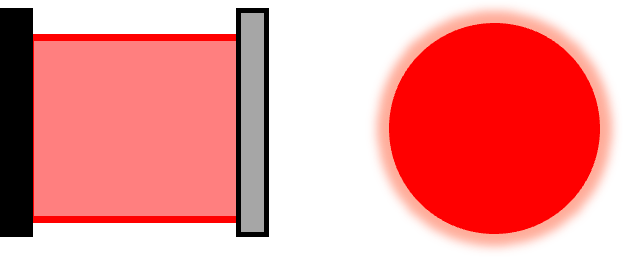 | Plano Reflector | Fine tilt | Creates a collimated beam perpendicular to a plano reflective target. |
| Catseye Single (CE-S) | 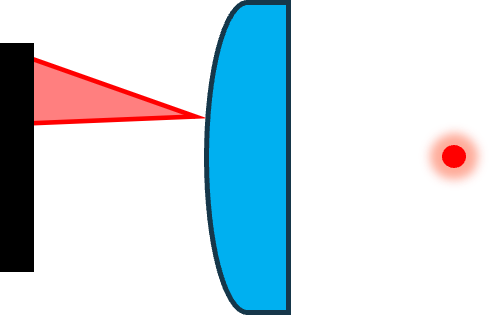 | UUT Surface | Coarse dX/dY Fine dZ | A single pattern focused on the UUT surface. The center ray from this pattern must arrive normal to the UUT surface. |
| Catseye Pair (CE-P) | 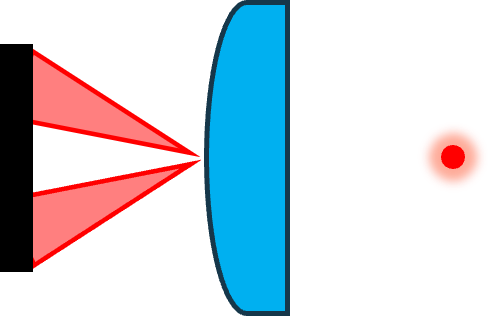 | UUT Surface | Coarse dX/dY Fine dZ | A pair of patterns are focused on the UUT surface. Light is sent from one pattern and is received by the other pattern. |
| Confocal Point Focus (PF-C) | 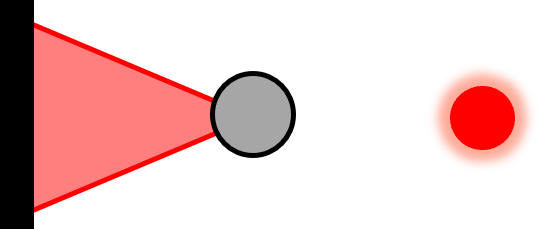 | Reflective Tooling Ball | Fine dX, dY, and dZ | Projects a focused spot to center of a reflective ball. |
| Crosshair Point Focus (PF-X) | 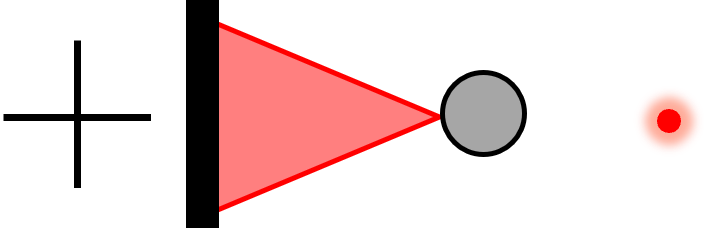 | Reflective Tooling Ball | Mid-range dX and dY Fine dZ | Projects a focused spot to vertex of a reflective ball. These patterns utilize a crosshair shadow overlay to provide lateral alignment feedback. |
| Line Focus Reference (LF-H, LF-V, LF-R, LF-T) | 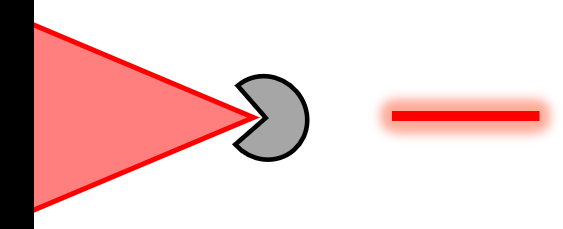 | Corner Cube, SMR | Fine alignment of dX OR dY; (Pairs of patterns can also align dZ and clocking) | Projects a line focus to specified retroreflector target. Provides alignment in a single degree of freedom (perpendicular to the line). LF-H, LF-V, LF-R, and LF-T specify Horizontal, Vertical, Radial, or Tangential orientation. |
| Arc Focus Reference (AF-H, AF-V, AF-R, AF-T) | 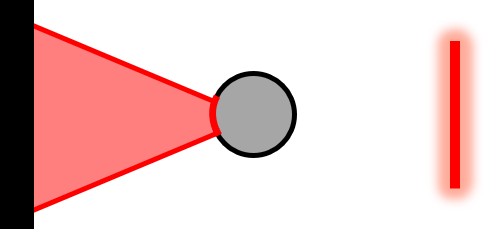 | Reflective Tooling Ball | Fine alignment of dX OR dY; (Pairs of patterns can also align dZ and clocking) | Projects a focused arc onto a curved reflective surface. Provides alignment in a single degree of freedom (along the line). AF-H, AF-V, AF-R, and AF-T specify Horizontal, Vertical, Radial, or Tangential orientation. |
A successful metrology solution includes a complementary set of alignment patterns that constrain all relevant alignment degrees of freedom from coarse to fine resolution. The table below illustrates how these various patterns can be utilized for your test optic.