Search Resources
-
CAD Models
-
- CAD Model: CGH-S9-C9_A.step
- CAD Model: CGH-S9-C0_A.step
- CAD Model: CGH-S6-C6_A.step
- CAD Model: CGH-S6-C0_A.step
- CAD Model: CGH-S3-C6_A.step
- CAD Model: CGH-S3-C3_A.step
- CAD Model: CGH-S3-C0_A.step
- CAD Model: C6XXXC_A.step
- CAD Model: C4XXXC_A.step
- CAD Model: C3XXXs_A.step
- CAD Model: C2XXXS-BC.step 2-Inch Cylinder CGH
-
-
Documentation
-
- Customer Drawing: MP6-BLANK_A
- Customer Drawing: MP3-BLANK_A
- Customer Drawing: VRT-050_A
- Customer Drawing: CRT-050_A
- Customer Drawing: C6AC3_A
- Customer Drawing: C6R_A
- Customer Drawing: FP9-H600_A
- Customer Drawing: FP6-H600_B
- Customer Drawing: FP6-H425_B
- Customer Drawing: FP3-Z-H600_B
- Customer Drawing: FP3-Z-H425_B
- Customer Drawing: FP3-H600_A
- Customer Drawing: FP3-H425_A
- Customer Drawing: CGH-S9-C9_A
- Customer Drawing: CGH-S9-C0_A
- Customer Drawing: CGH-S6-C6_A
- Customer Drawing: CGH-S6-C0_A
- Customer Drawing: CGH-S3-C6_A
- Customer Drawing: CGH-S3-C3_A
- Customer Drawing: CGH-S3-C0_A
- Customer Drawing: C6XXXC_A
- Customer Drawing: C4XXXC_A
- Customer Drawing: C3XXXS_A
- Customer Drawing: C2XXXS-BC 2-Inch Cylinder CGH
- Customer Drawing: FP6-Z-H650_A
- Show Remaining Articles ( 10 ) Collapse Articles
-
-
Publications
-
- [2023] New Applications of Computer Generated Holograms for Optical Testing
- [2023] Rapid surface metrology of freeform shapes using CGH interferometry
- [2022] Snapshot measurements with CGH interferometry to support volume production of freeform optics
- [2022] Computer generated hologram (CGH) education kit for hands-on learning of optical metrology for complex optics and systems
- [2022] CGH-assisted metrology testbed for the Thirty Meter Telescope primary mirror
- [2021] Metrology Testbed for the Thirty Meter Telescope Primary Mirror
- [2019] Interferometric Metrology for the TMT Primary Mirror Segments: Design and Analysis
- [2018] Infrared computer-generated holograms: design and application for the WFIRST grism using wavelength-tuning interferometry
- [2016] Optical Alignment with CGH Phase References
- [2014] Precision Alignment And Calibration Of Optical Systems Using Computer Generated Holograms
- [2014] Diffractive optics calibrator: measurement of etching variations for binary computer-generated holograms
- [2013] Optical testing with computer generated holograms: comprehensive error analysis
- [2013] Design and analysis of an alignment procedure using computer-generated holograms
- [2011] Low uncertainty alignment procedure using computer generated holograms
- [2010] Imaging issues for interferometry with CGH null correctors
- [2010] Measurement of aspheric mirror segments using Fizeau interferometry with CGH correction
- [2009] Fizeau interferometer with spherical reference and CGH correction for measuring large convex aspheres
- [2007] Fabrication error analysis and experimental demonstration for computer-generated holograms
- [2007] Optical alignment with computer-generated holograms
- [2007] Optimal design of computer-generated holograms to minimize sensitivity to fabrication errors
- [2007] Coupling of surface roughness to the performance of computer-generated holograms
- [2006] Analysis of phase sensitivity for binary computer-generated holograms
- [2006] Absolute calibration of null correctors using twin computer-generated holograms
- [2006] Use of computer generated holograms for alignment of complex null correctors
- [2005] Testing an off-axis parabola with a CGH and a spherical mirror as null lens
- [2004] Efficient testing of segmented aspherical mirrors by use of reference plate and computer-generated holograms. I. Theory and system optimization
- [2004] Efficient testing of segmented aspherical mirrors by use of a reference plate and computer-generated holograms. II. Case study, error analysis, and experimental validation
- [1999] Efficient testing of off-axis aspheres with test plates and computer-generated holograms
- [1999] Error analysis for CGH optical testing
- [1999] Diffraction wavefront analysis of computer-generated holograms
- [1995] Applications of computer-generated holograms for interferometric measurement of large aspheric optics
- Show Remaining Articles ( 16 ) Collapse Articles
-
-
FAQs
-
- What is a CGH?
- How are CGHs used?
- What is a "null"?
- What is a "UUT"?
- How is a CGH mounted and adjusted?
- What types of surfaces can be measured using a CGH?
- What is the typical accuracy of a CGH?
- What are the benefits of using a CGH for metrology?
- What is CGH substrate error and how does it get subtracted?
- What are fiducial dots and how are they used?
- Are CGHs delicate?
- How do you clean a CGH?
- What is a Metrology Platform?
- What type of interferometer do I need to use a CGH?
- What is diffraction efficiency?
- What is the difference between an amplitude and a phase CGH?
- How is a CGH different from other types of holograms?
- What size CGHs does AOM produce?
- Do CGHs require regular calibration?
- Show Remaining Articles ( 4 ) Collapse Articles
-
-
How-To's
-
Technologies
-
-
- Arc Focus Reference Alignment Patterns (AF)
- Crosshair Point Focus (PF-X)
- Line Focus Reference Alignment Patterns (LF)
- Confocal Point Focus Alignment Pattern (PF-C)
- Catseye Pair Alignment Pattern (CE-P)
- Catseye Single Alignment Pattern (CE-S)
- Collimation Alignment Pattern (CO)
- Visual Point Focus Alignment Pattern (PF-V)
-
-
What is diffraction efficiency?
Diffraction efficiency (DE) is the percentage of light sent into a particular diffraction order. Diffraction efficiency depends on a variety of factors:
- Amplitude or phase CGH
- Duty cycle
- (Phase CGH only): Depth of structures, material refractive index, and test wavelength
What are the diffraction efficiency equations?
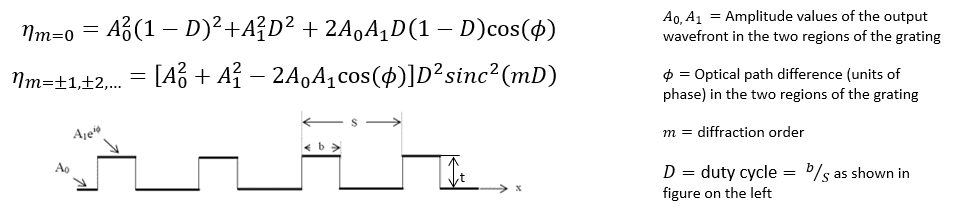
where we use the normalized sinc function: sinc(x) = sin(πx) / πx
What diffraction efficiency do CGHs from AOM typically have?
- Typical diffraction efficiency in the 1st diffraction order for an amplitude CGH with 50% duty cycle is ~10%.
- Typical diffraction efficiency in the 1st diffraction order for a phase CGH with 50% duty cycle and structure depth of λ/2(n-1) is ~40%*. (λ=test wavelength, n=refractive index of structure).
*Note: AOM requires a nonzero percentage of diffraction efficiency in the 0 order to measure a Transmitted Wavefront Error map of the substrate. To do this, etch depth is modified to reduce DE in the 1st (design) order and add diffraction efficiency to the 0 order.
Table of Contents